
 SUPPLY MANAGEMENT ARTICLE: JLR will trace raw materials from ‘origin to supplier’ Blockchain-based technology is starting to gain traction in business. Jaguar Land Rover, Mercedes-Benz, UAE government are some of the brands evaluating the many benefits…
SUPPLY MANAGEMENT ARTICLE: JLR will trace raw materials from ‘origin to supplier’ Blockchain-based technology is starting to gain traction in business. Jaguar Land Rover, Mercedes-Benz, UAE government are some of the brands evaluating the many benefits…
The Blockchain is an undeniably ingenious invention – the brainchild of a person or group of people known by the pseudonym, Satoshi Nakamoto. Original devised for the digital current Bitcoin it has since evolved into something greater and the tech community has now found other potential uses for the technology.
 By allowing digital information to be distributed but not copied, Blockchain technology creates the backbone of a new type of internet. Simplified, Blockchain is a time-stamped series of immutable record of data managed by a cluster of computers not owned by a single entity. Each of these ‘blocks’ of data are secured and bound to each other using cryptographic principles (i.e.: chain).
By allowing digital information to be distributed but not copied, Blockchain technology creates the backbone of a new type of internet. Simplified, Blockchain is a time-stamped series of immutable record of data managed by a cluster of computers not owned by a single entity. Each of these ‘blocks’ of data are secured and bound to each other using cryptographic principles (i.e.: chain).
“The Blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be
programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.”
Don & Alex Tapscott authors: Blockchain Revolution (2016)
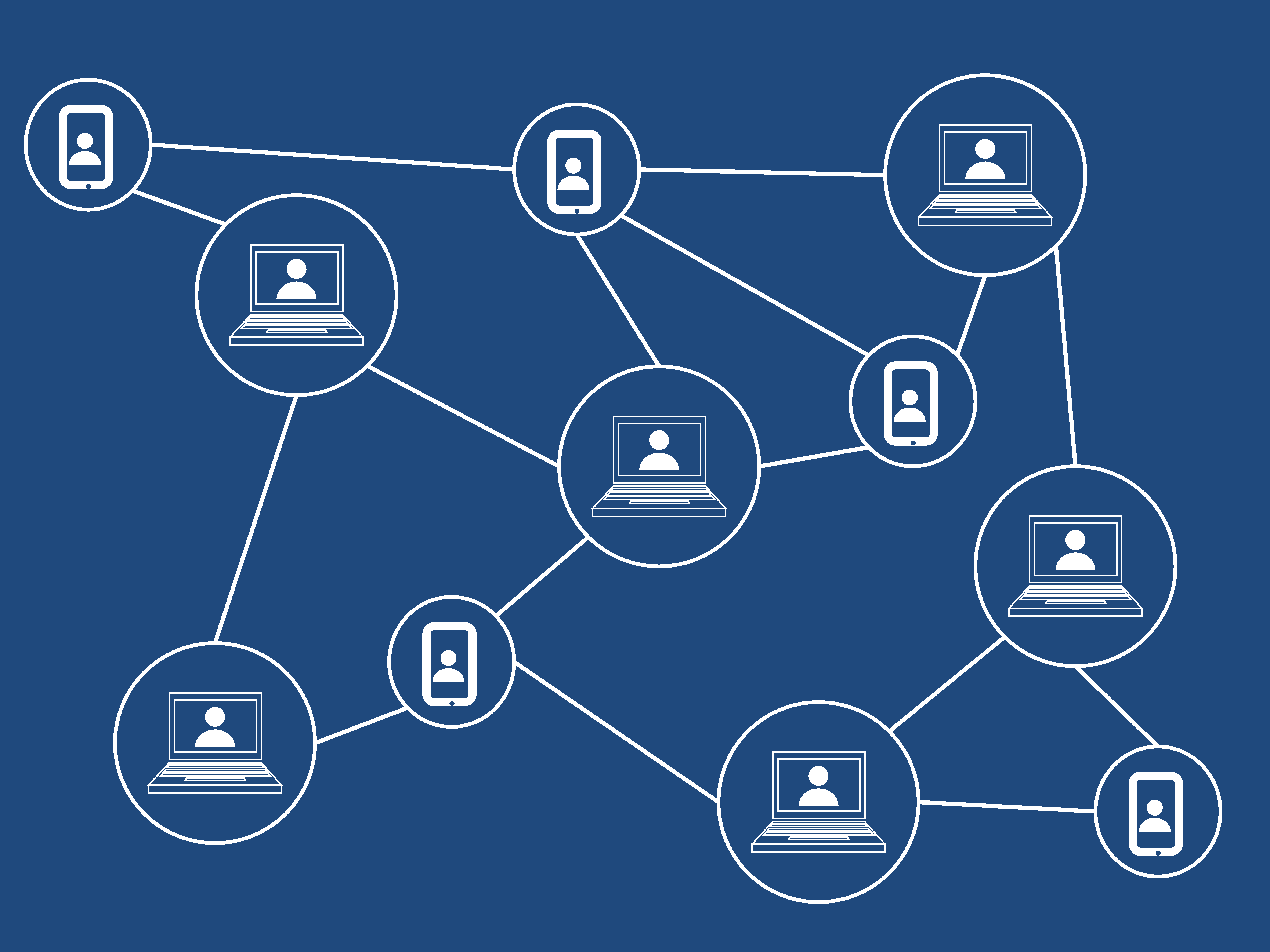
The Blockchain network has no central authority — it is the very definition of a democratised system. Since it is a shared and immutable ledger, the information in it is open for anyone and everyone to see. Hence, anything that is built on the Blockchain is by its very nature transparent and everyone involved is accountable for their actions.
Picture a spreadsheet that is duplicated thousands of times across a network of computers. Then imagine that this network is designed to regularly update this spreadsheet and you have a basic understanding of the Blockchain. The Information held on a Blockchain exists as a shared — and continually reconciled — database. This is a way of using the network that has obvious benefits.
The Blockchain database isn’t stored in any single location, meaning the records it keeps are truly public and easily verifiable. No centralised version of this information exists for a hacker to corrupt. Hosted by millions of computers simultaneously, its data is accessible to anyone on the internet.
To understand Blockchain we must understand the three pillars the technology is based on:
Before Bitcoin came along, we were more used to centralised services. The idea is very simple. You have a centralised entity which stored all the data and you’d have to interact solely with this entity to get whatever information you required. The traditional client-server model is a perfect example of this. Centralised systems have treated us well for many years; however, they have several vulnerabilities.
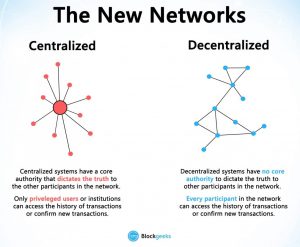
In a decentralised system, the information is not stored by one single entity. In fact, everyone in the network owns the information. In a decentralised network, if you wanted to interact with your friend then you can do so directly without going through a third party. That was the main ideology behind Bitcoins. You and only you alone are in charge of your money. You can send your money to anyone you want without having to go through a bank.

One of the most interesting and misunderstood concepts in Blockchain technology is “transparency.” Some people say that Blockchain gives you privacy while some say that it is transparent. While a person’s identity is hidden via complex cryptography and represented only by their public address. So, while the person’s real identity is secure, you will still see all the transactions that were done by their public address.
This level of transparency has never existed before. It adds that level of accountability which is required. If for example you know the public address of one of the big manufacturing companies, you can simply pop it in an explorer and look at all the transactions that they have engaged in. This forces everyone to be honest and eliminates counterfeiting, proves origin and so other huge benefits in the supply chain.
Immutability, in the context of the Blockchain, means that once something has been entered into the Blockchain, it cannot be tampered with. The reason why the Blockchain gets this property is that of cryptographic hash function. In simple terms, hashing means taking an input string of any length and giving out an output of a fixed length. In summary instead of just containing the address of the previous block it also contains the hash of the data inside the previous block.
While technical there is just one property that you need to be aware of and it is called the “Avalanche Effect.” If someone tries to change data because of the properties of hash functions, a slight change in data will change the hash drastically. This means that any slight changes made in block 3, will change the hash which is stored in block 2, now that in turn will change the data and the hash of block 2 which will result in changes in block 1 and so on and so forth. This will completely change the chain, which is impossible. This is exactly how Blockchain attain immutability.
Blockchain technology presents a significant step-change in business solutions for the Supply Chain:
 Our worldwide patented Unique Referencing (UR) mechanism is the backbone of our product suite and is based on the unique and innovative principles of what has became Blockchain.
Our worldwide patented Unique Referencing (UR) mechanism is the backbone of our product suite and is based on the unique and innovative principles of what has became Blockchain.
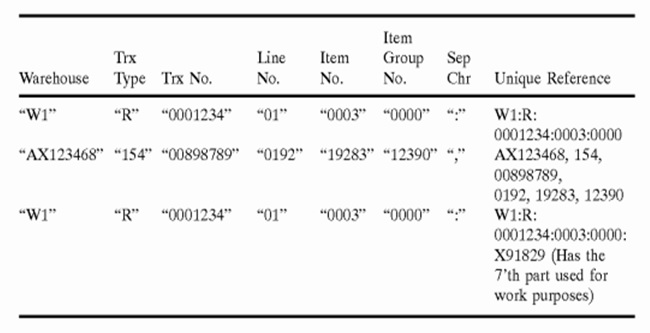
ProWMS Warehouse Management Software: Unique Referencing mechanism code description
We just love to develop innovative solutions that improve on our customer’s operations and ROI. If you’re experiencing Warehousing or Supply Chain operation issues or bottlenecks – or just need improvements to stay ahead of the competition – then ask us how, today.
Acknowledgements: The above text and images are a summary of one of the best articles on Blockchain I have read to date. This is from an Article by Ameer Rosic entitled “What is Blockchain Technology? A Step-by-Step Guide For Beginners” and published here.
* Source: Blockgeeks